| Outstanding Cases VOL.5 | Danxiashan and Cangdong Center (China) |
| PublishDate:2021-10-27 Hits:4500 |
I. Background World Heritage Education (WHE) is not only one of the most important ways to connect people to world heritages, but also a key to a creative solution for sustainable development of the heritage sites. With the accelerated development of the Internet technology in recent years, more and more innovators have accessed the heritage education field. They have not only promoted the regeneration of the contents and methods of heritage education, but also make it possible for heritage education to break existing boundaries and modes.
To correspond to and promote this reform, WHITRAP initiated this Global Innovation Cases of World Heritage Education in the hope to have a fine collection of forward-looking exemplar heritage education cases. The aim is to promote the sharing of relevant international experience and future cooperation, and contribute to the comprehensive and sustainable development of heritage sites. Cases were expected to be characterized essentially by global demonstrativeness which was further supported by four professional criteria of innovation, technology, cooperation and sustainability.
After a month-long application, candidate cases entered the selection stage and were officially presented at the 44th Session of the World Heritage Committee. This initiative received enthusiastic responses from all parties, and WHC’s official website also published WHITRAP’s global call for case studies on World Heritage Education. This initiative has received warm responses from all parties. Nearly 100 WHE innovation cases were collected from five continents of the world within a month, highlighting the emerging trends in various innovation fields and providing an important reference to explore the topic in the future. With reference to future development and model innovation as a global model, five qualities of future-oriented WHE are summarized as follows:
1) Enhancing social inclusiveness and cohesion via heritage education especially for the youth based on heritage protection;
2) Promoting multi-disciplinary integration through cross-boundary innovations and exploring a new model of multi-party cooperation through internal and external combination;
3) Exploring new heritage education concepts and methods according to local conditions via creativity and technology;
4) Rationalizing the use of Internet and digital technology to involve more people online and offline in heritage education;
5) Discovering heritage values and using education as an empowering tool to promote the creative innovative and sustainable development of heritage sites.
Based on the five qualities, the collection of 10 outstanding cases will present their innovation and exemplary significance. Those cases demonstrate a wide range of possibilities of the future WHE from the perspectives of life-time education, digitalization, cyber technology, cultural tourism development, world peace, social integration and philosophy, representing the emerging trends in various innovation fields. The thought-provoking cases provide a guideline for us to explore possible actions for the future WHE development. In the series of the presentation of outstanding cases, we will focus on the educational activities for world heritage sites or specific heritage values, presenting their practical effects and valuable lessons over the past five years.
In the last issue, from the two cases from China, we have learned their experience of “rationalizing the use of Internet and digital technology to involve more people online and offline in heritage education”. This issue will involve two cases: “Innovative Exploration and Practice of World Heritage Education of Danxiashan” and “Cangdong Heritage Education Center” (China, Guangdong). Let’s discover their innovative features in “discovering heritage values and using education as an empowering tool to promote the creative innovative and sustainable development of heritage sites”.
II. Presentation of Outstanding Cases VOL.4
1. Innovative Exploration and Practice of World Heritage Education of Danxiashan (China, Guangdong)
1) Introduction
In August 2020, “China Danxia”, a serial World Heritage nomination comprising six Danxia landscape nominated sites in six provinces of China, represented by Danxiashan in Guangdong Province, was listed on the World Heritage list at the 34th Session of World Heritage Committee. After nearly ten years of practice, it has gradually formed a five-dimensional goal model of heritage education for “managers, community residents, tourists, students and the public”, a “big community” development model of the cooperation between higher authorities, community residents, universities, research institutes, local enterprises, visitors, and local governments.
This model has made phased achievements. First, it has expanded the target audience of heritage education, realized the full coverage of heritage education for different ages, and deepened the public’s understanding and recognition of the world heritage value of Danxiashan. Second, under the guidance of heritage education, new tourism methods such as field study trips and science popularization tours are explored to promote the upgrading of the tourism industry of the heritage site. Finally, community residents get intellectual, economic and social empowerment by receiving heritage education and participating in heritage protection. They get more diverse ways of living as their tourism participation has been upgraded through participating in field study trips and science popularization tours. Benefits have been obtained from protection, and community residents have enhanced their local recognition and sense of achievement.
The heritage education of the Danxiashan World Heritage site has made phased achievements, and the advantages of the multi-cooperation mechanism have been gradually highlighted. It has set up a “Danxia Think Tank” composed of nearly 100 experts from colleges and universities, serving for heritage education. It has formed a sound knowledge supply system for scientific research and heritage education, developed more than 200 heritage education courses, cultivate a team of 600 science volunteers, transformed and upgraded a group of local farmers into “science popularization talent”. Heritage education brands such as “Danxiashan Science Popularization Town” and “Danxiashan Wild Plant Identification Competition” have been established. Annually, more than 400,000 people go to the heritage site to receive heritage education. The achievements have been appraised during the 1st and 2nd World Heritage revalidations. Experts, scholars and managers in protected areas from Russia, Thailand, Scotland and more than 20 provinces and cities in China have been attracted to come. Danxiashan provides experience for other heritage sites to carry out heritage education. It has gradually become a “Chinese model” for world heritage education.
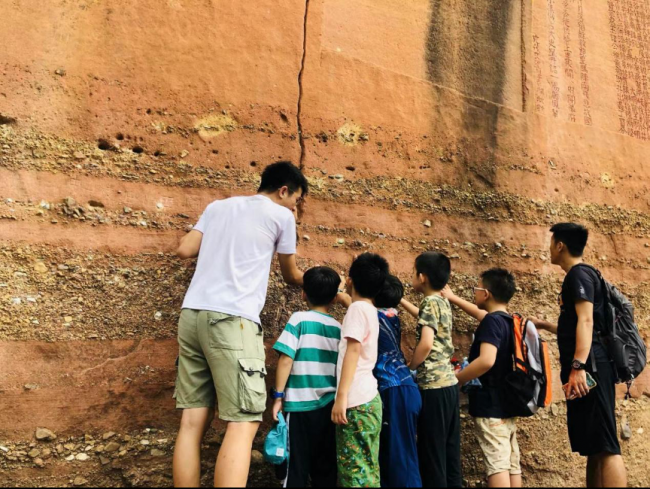 The science tour guide introduced heritage education in Danxia Mountain
2) Innovation
According to the mission of the World Heritage Convention, Danxiashan has explored and innovated the concepts and methods of heritage education based on its resource advantages. It has formed a five-dimensional goal model of heritage education oriented to “managers, community residents, tourists, students and the public”, which breaks through most heritage education’s limitation to students’ education in the past.
Internally, Danxiashan has taken many measures to enhance management and community residents’ understanding of the heritage value as well as improved their heritage protection skills through training and learning. For example, it invited experts from different disciplines in scientific research institutes or universities such as Sun Yat-sen University and China University of Geosciences to give lectures on geology and geomorphology, biodiversity, cultural relic protection and environmental monitoring. Externally, it has adopted the heritage education mode of “going out” and “inviting in”. Danxiashan has successively launched two large-scale public welfare lecture activities, such as “China Danxia on Campus” and “Danxiashan: Spectacular Nature in the World Book Crossing” since 2010. Nearly 400 lectures have been carried out in more than 300 primary schools, secondary schools, universities, conferences and forums in many countries, benefiting 200,000 audiences.
Danxiashan attaches great importance to the use of creative and technological means to serve the exploration and publicity of heritage value, and actively strengthens cooperation with universities and technological enterprises. Besides, it has also taken advantages of the convenience of the information era, explored the mode of “Internet + Science Popularization”, and persisted in holding a series of online lectures on science popularization of Danxiashan’s value through the trill. Especially during the COVID-19 epidemic in 2020, online science popularization lectures and “Cloud Tour of Danxiashan” were successively held, with a total number of nearly 300,000 participants.
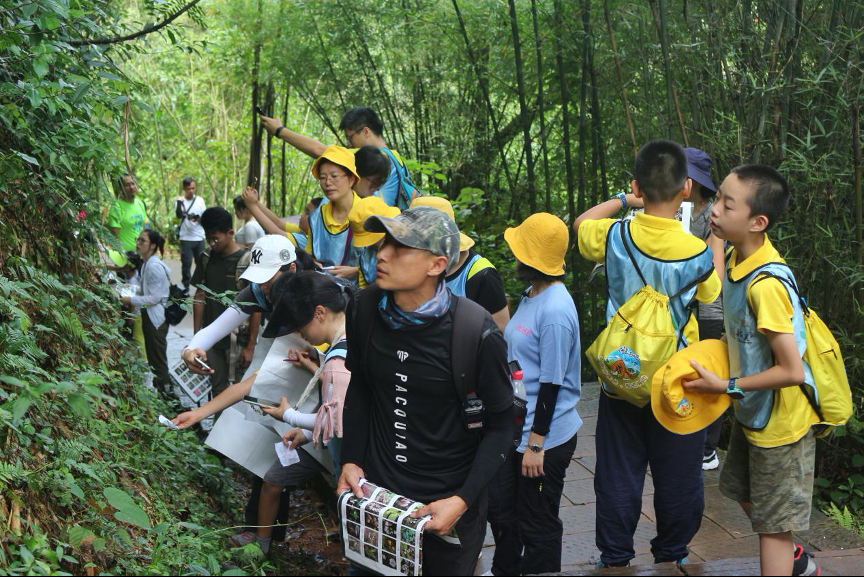 Danxiashan Wild Plant Identification Competition
3) Sustainability
The work innovation under the guidance of Danxiashan heritage education has also promoted the sustainable development of the heritage site. Danxiashan Administrative Committee has explored the innovation of community participation in developing heritage sites under the concept of heritage education,new forms of development such as research travel and science popularization tourism have been introduced.
Danxiashan has signed cooperation agreements with more than 30 domestic universities to provide support for heritage residents to understand the value of heritage through scientific research in colleges and universities. Since 2014, a team of more than 600 science popularization volunteers has been organized to help community residents transform and upgrade. Danxiashan Nature School was established in 2017 to provide the community with opportunities to participate in the research industry. In 2019, Danxiashan further integrated resources, innovatively put forward the concept of “Science Popularization Town” and “Science Popularization School” and put it into practice. So far, nearly 30 inns and guesthouses have joined the “Science Popularization School” project, participating in the new development model of Danxiashan tourism.
Danxiashan’s exploration under the framework of heritage education has set up a chain of local knowledge delivery by university experts and science popularization volunteers, prompting the original residents to enhance their recognition and support for the heritage sites as well as to acquire more skills. Farmers including “Uncle Dendrobium” have become “Science Popularization Enthusiasts”. Meanwhile, through the exploration of field study trips, science popularization tourism and other development methods, the residents who were originally engaged in general tourism service began to turn to knowledge service-oriented tourism, providing community residents with more diverse livelihood options.
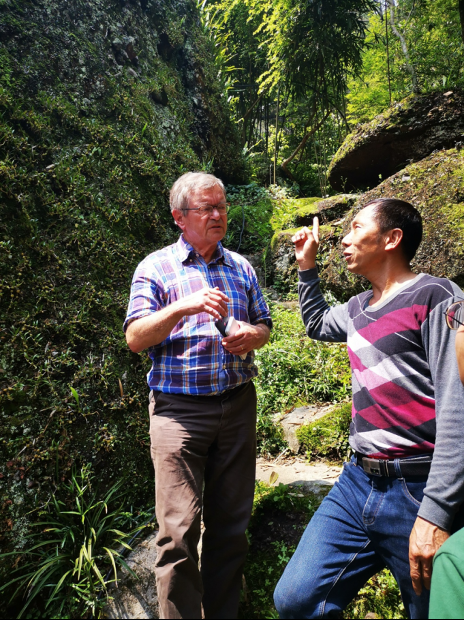 “Uncle Dendrobium” introduced the Dendrobium planting experience to foreign experts
2. Cangdong Heritage Education Center (China, Guangdong)
1) Introduction
The “Cangdong Project” was started in 2009 and is managed by the social enterprises “Kaiping City Cangdong Cultural Heritage Conservation and Development Center”. It cooperates with villagers, relies on local culture, takes heritage education as a means of development, helps local and surrounding residents to create traditional communities, establishes a sense of belonging and identity among local people. It not only provides visitors with opportunities for experience and education, but also establishes links and respect between urban and rural residents. The project is also a platform for integrating heritage conservation resources, seeking community development in a way of sharing.
The educational activities of Cangdong Heritage Education Center are based on the local cultural experience dominated by the villagers, which is in line with the real life of the villagers to the maximum extent, and the experience is the basic educational method. The project explores the adaptive regional practice of successful experiences in different parts of the world in China, and explore the heritage experiential education curriculum and management methods adapted to the needs of society.
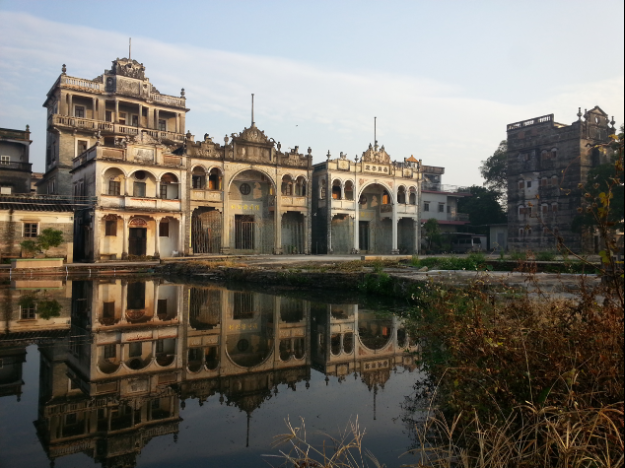 Restored Cangdong - Maintaining the natural landscape of the countryside
2) Innovation
The mechanism of cooperation among Wuyi University, social enterprise and village committee was established: university scholars are academic leaders, Cangdong social enterprise is in charge of local management, and villagers are the main participants in the field. Based on geographical advantages, the project has established a shared community platform and joint practice position, and carried out theoretical exploration and academic accumulation.
Five small museums with different themes have been established to present the value of Cangdong to the audience in combination with sound and photovoltaics. A cloud system, GPS and a database have been established to facilitate search, mobile phone mini-programs have been developed, for visitors to have a deeper understanding of heritage knowledge and heritage training activities in Cangdong.
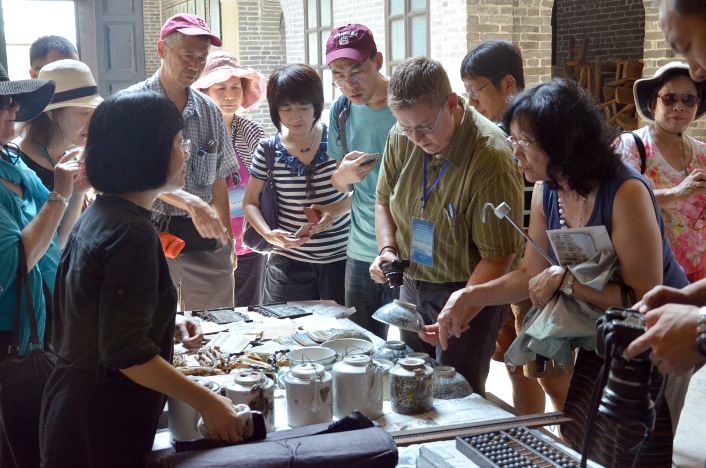 Tourists explored ceramics in Cangdong Heritage Education Center
3) Sustainability
The project has established a heritage education platform that integrates resources to help residents build a sense of belonging, preserve local culture and play an active role in the project. The project takes social enterprises as the operating management organization to carry out educational activities. Thus, the project income can ensure its daily operation. At the same time, in cooperation with the Qianhe Foundation in Guangzhou, a special fund for heritage conservation has been set up to connect social donations.
In Cangdong, the project has adhered to the development direction of heritage conservation and social value, supplemented by economic benefits. The project takes the creation of a community dominated by the civil power and bottom-up community building as a development goal, fully integrates all sectors of society, encourages public participation, and forms a community of heritage conservation, heritage adaptive reuse, and heritage education.
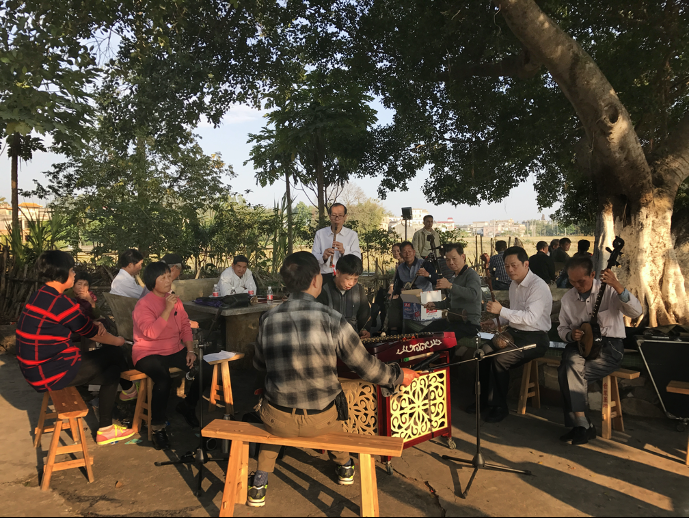 Villagers played folk music in Cangdong
 Foreign friends learned calligraphy in the ancestral hall
III. Conclusion
In this issue of the presentation of outstanding cases, two case studies from China demonstrate the useful experience of discovering heritage values and using education as an empowering tool to promote the creative innovative and sustainable development of heritage sites. These programs not only enhance the public’s enthusiasm in promoting heritage education through participating in heritage education training and heritage protection actions, but also build a platform to provide comprehensive services for all stakeholders and improve the operation mode of multi-cooperation.
The series of Global World Heritage Education Innovative Cases have been completely presented. We sincerely wish heritage education practitioners and participants could learn from and get inspired by this presentation of outstanding cases. It would be encouraging to us if the five features summarized above could provide insights to tailor-made innovation practices in the future. The completion of the case collection marked yet another beginning. In the future, we will continue our efforts from here and make endeavors to establish an international network for WHE cooperation and exchange, thus contributing to the innovation of heritage education and the all-around and sustainable development of the heritage sites.
Contributed by: WHITRAP Working Group
Edited by: He Yixuan, Zhang Yiyang |
- News | WHITRAP Shanghai and CNR-ISPC bilateral meeting
- News | WHITRAP meets Cité de l’Architecture et du Patrimoine
- WHITRAP Hosting "Workshop on Preliminary Assessment for National Focal Points of the Asia Region" in Chengdu
- WHITRAP Shanghai meets UNESCO
- INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE PRELIMINARY ANNOUNCEMENT & CALL FOR PAPERS
- Observation of the 46th Session of the World Heritage Committee
Copyright © 2009-2012 World Heritage Institute of Training and Research-Asia and Pacific (shanghai)